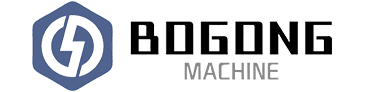Laser Cleaning Machine Applications: A Complete Industrial Guide to Where, Why, and How It Is Used

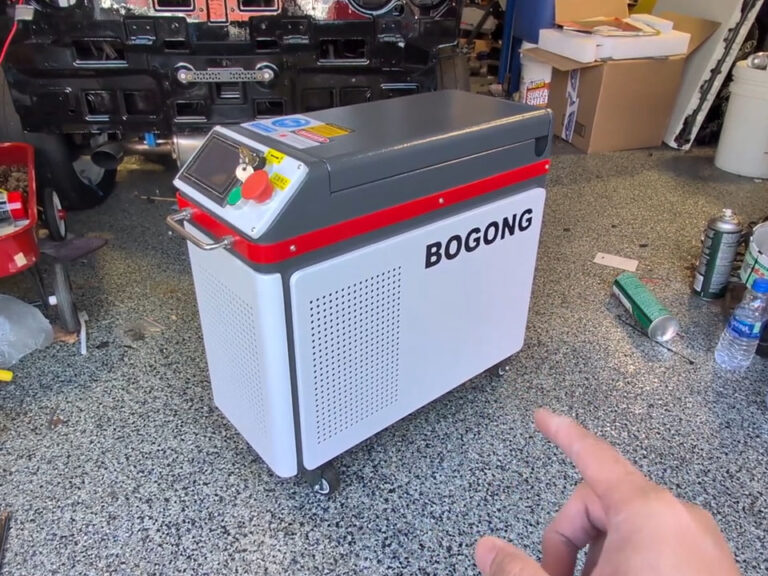
Laser cleaning machines are often introduced as a “new cleaning method,” but in real industrial practice they function as something much broader: a precision surface treatment technology that replaces or complements sandblasting, chemical stripping, grinding, and solvent cleaning across a wide range of industries. Understanding laser cleaning applications is not about memorizing a list; it is about recognizing where surface cleanliness, control, and repeatability create tangible value.
Laser cleaning machines are applied wherever surface contaminants must be removed accurately, consistently, and with minimal impact on the base material—especially in environments where waste, rework, downtime, or surface damage carry high cost. This guide presents a comprehensive, application-driven view of laser cleaning across industries, materials, and process stages, written for engineers, manufacturers, and decision-makers rather than casual observers.
1. Corrosion and Rust Removal in Heavy Industry and Maintenance
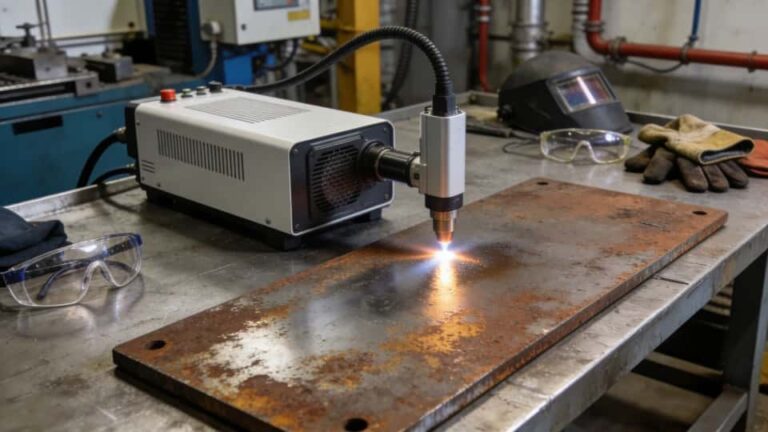
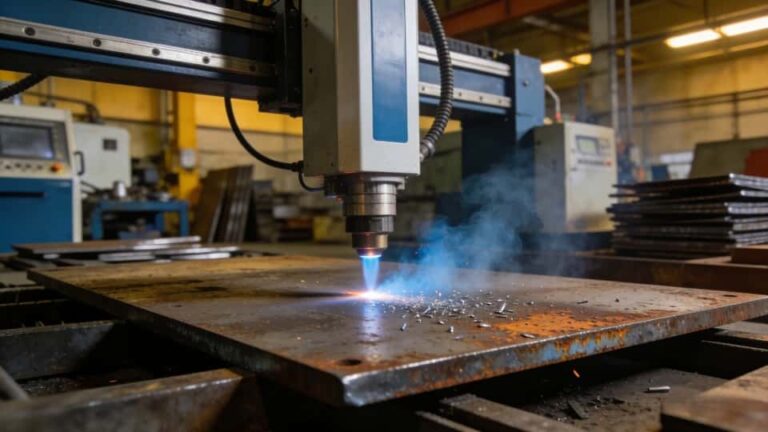
Rust removal remains the most visible and widely adopted application of laser cleaning, particularly in heavy industry, infrastructure maintenance, and equipment refurbishment. Steel corrosion products absorb laser energy efficiently, while the underlying metal reflects or dissipates much of it. This natural contrast creates a stable and forgiving cleaning window.

Laser cleaning is used to remove:
- Light surface rust (flash rust)
- Medium to heavy corrosion layers
- Oxide scale on hot-rolled steel
- Localized corrosion around welds and fasteners
- Corrosion in difficult geometries without disassembly
In heavy industry, laser rust removal is applied in:
- Steel structure maintenance
- Power plants and substations
- Oil and gas facilities
- Shipbuilding and offshore platforms
- Bridges, cranes, and industrial frameworks
Compared with sandblasting, laser cleaning offers localized treatment, reduced masking, and minimal secondary waste. It is particularly valuable where only specific areas require cleaning and full blasting would be excessive or disruptive.
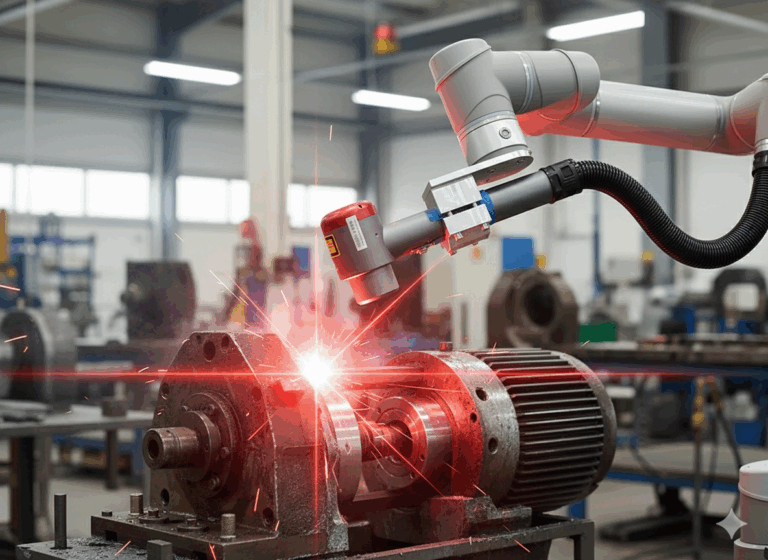
2. Paint, Coating, and Surface Layer Removal
Paint and coating removal is one of the fastest-growing laser cleaning applications, especially in industries where selective removal is required. Unlike chemical stripping or abrasive blasting, laser cleaning can be tuned to remove specific layers while leaving others intact.
Laser cleaning machines are used to remove:
- Industrial paints
- Epoxy and polyurethane coatings
- Powder coatings
- Anti-corrosion layers
- Surface markings and functional films
This capability is widely applied in:
- Aerospace maintenance and repair
- Automotive manufacturing and refurbishment
- Rail and transportation equipment
- Shipbuilding and marine maintenance
- Heavy equipment remanufacturing
A key advantage is layer selectivity. With appropriate parameter control, operators can remove top coats without damaging primers or substrates. This reduces rework, preserves dimensional integrity, and shortens turnaround time.
3. Welding Preparation and Post-Weld Cleaning
Welding-related applications represent some of the highest-value uses of laser cleaning machines. Weld quality is highly sensitive to surface condition, particularly the presence of oxides, oils, and residues.
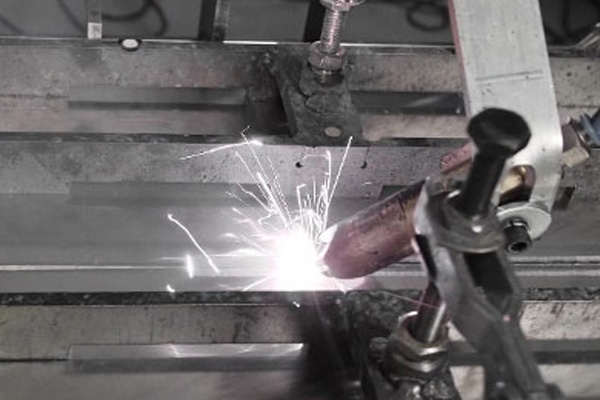

Laser cleaning is used before welding to:
- Remove oil, grease, and machining fluids
- Eliminate oxides on steel and aluminum
- Clean weld seams and joint edges
- Prepare battery tabs and busbars
After welding, laser cleaning is applied to:
- Remove heat tint on stainless steel
- Clean post-weld oxidation
- Improve cosmetic appearance
- Prepare surfaces for subsequent coating or inspection
Industries using laser cleaning for welding applications include:
- Automotive and EV manufacturing
- Battery and energy storage production
- Aerospace structures
- Pressure vessel and piping fabrication
- Precision metal fabrication
By improving weld consistency and reducing porosity, laser cleaning delivers value that far exceeds the cost of the cleaning step itself.
4. Mold, Tool, and Die Cleaning in Manufacturing
One of the most economically compelling laser cleaning applications is mold and tool maintenance. In injection molding, rubber processing, and die casting, residue buildup directly reduces product quality and tool life.
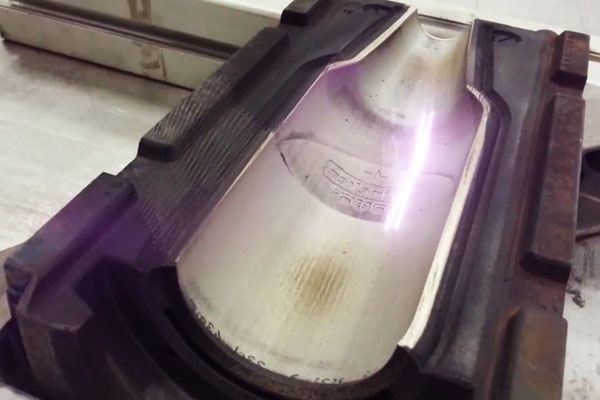

Laser cleaning removes:
- Carbonized polymer residues
- Rubber deposits
- Release agents
- Oil and additive buildup
- Fine contaminants in mold textures
Common users include:
- Plastic injection molding factories
- Rubber and tire manufacturing plants
- Die casting operations
- Composite molding facilities
Laser cleaning enables molds to be cleaned in place, often without disassembly. This reduces downtime, avoids abrasive damage, and preserves fine surface textures that are critical to product quality. Over time, extended mold life alone can justify the investment.
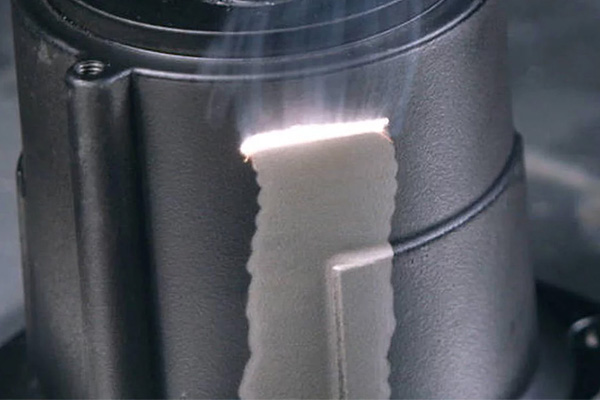
5. Degreasing and Organic Contaminant Removal
Laser cleaning is increasingly used as a dry degreasing process in manufacturing environments where chemical solvents are undesirable or restricted.
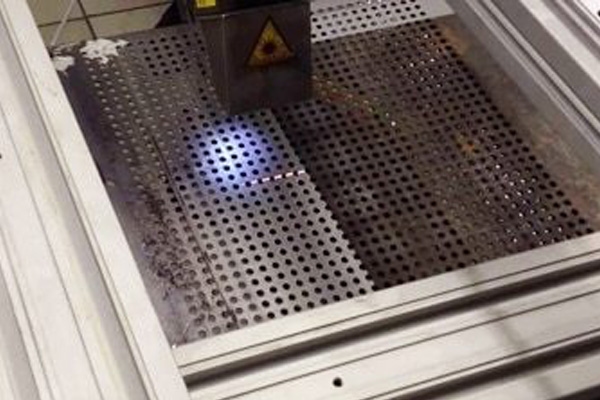
It effectively removes:
- Oils and lubricants
- Cutting and machining fluids
- Grease films
- Assembly residues
- Organic surface contaminants
This application is common in:
- Automotive manufacturing
- Precision machining
- Coating and painting lines
- Electronics and battery production
Laser degreasing leaves no chemical residue and integrates well into automated production lines. Proper fume extraction is essential, but when implemented correctly, the process improves cleanliness consistency and reduces solvent handling requirements.
6. Surface Preparation for Coating, Bonding, and Painting
Surface preparation is not only about removal—it is about creating a consistent, activated surface for downstream processes. Laser cleaning is increasingly used before painting, coating, or adhesive bonding.
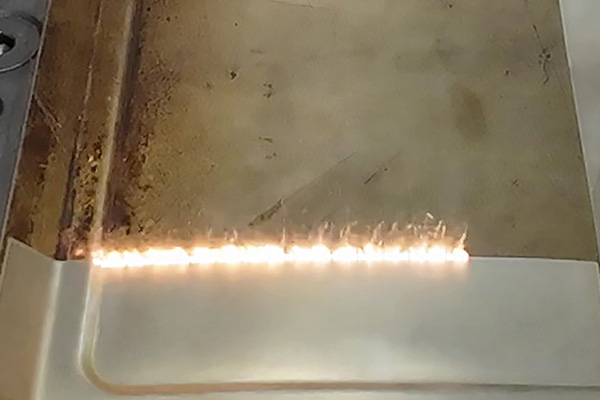

Applications include:
- Pre-paint cleaning of metal components
- Adhesive bonding preparation
- Sealant application surfaces
- Composite bonding interfaces
Laser cleaning provides:
- Clean, contaminant-free surfaces
- Consistent surface energy
- Minimal embedded particles
- High repeatability
While laser cleaning does not always replace abrasive profiling, it often complements or improves coating performance where cleanliness is more critical than roughness.
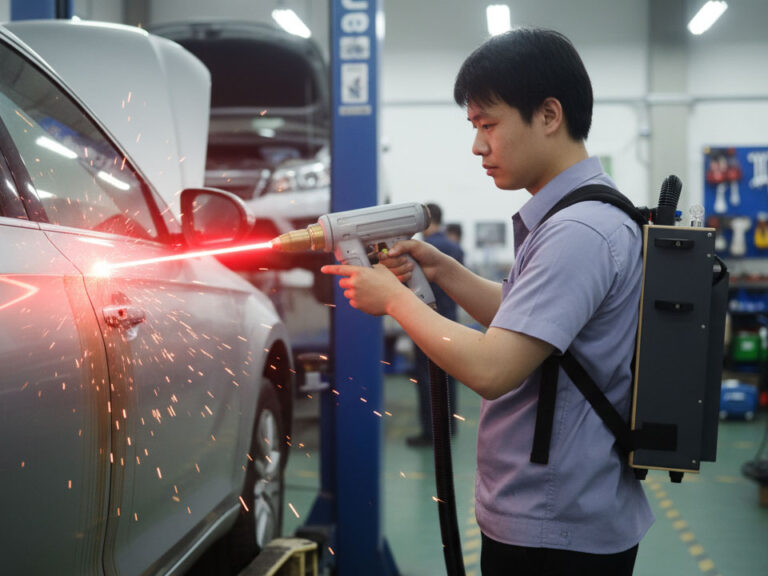
7. Industrial Maintenance, Repair, and Refurbishment
Laser cleaning machines are widely adopted in maintenance and repair scenarios where flexibility and minimal disruption are required.
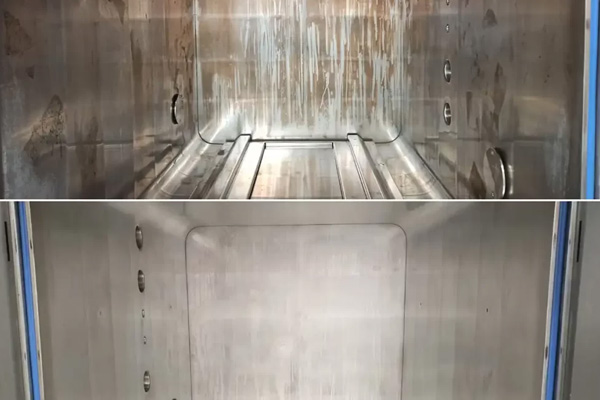

Typical maintenance applications include:
- Equipment refurbishment
- Bearing seats and housings
- Flange face cleaning
- Surface preparation during shutdowns
- On-site corrosion treatment
In these environments, the ability to bring a portable laser cleaner to the job—rather than disassembling components or transporting them to blasting facilities—delivers significant time and cost savings.
8. Precision and High-Value Component Cleaning
In industries where parts are expensive and tolerances are tight, laser cleaning provides a non-contact, controlled alternative to mechanical methods.
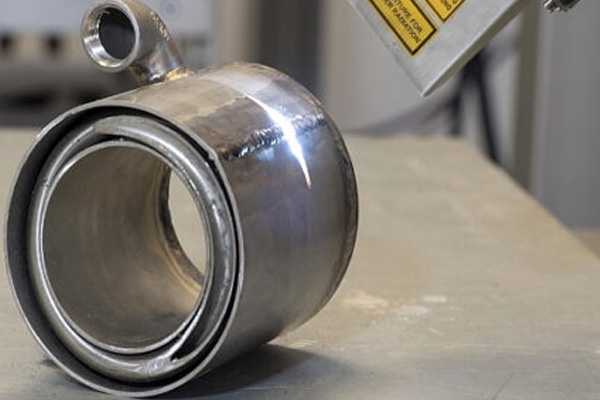

Applications include:
- Aerospace components
- Medical device manufacturing
- Precision mechanical assemblies
- Optical and sensor housings
- High-performance alloys
Here, the value of laser cleaning lies in damage avoidance. Preserving surface integrity, dimensional accuracy, and microstructure is often more important than cleaning speed.
9. Heritage, Restoration, and Specialized Applications
Beyond heavy industry, laser cleaning is also used in specialized and niche fields, including:
- Heritage stone and monument restoration
- Art conservation
- Historical metal artifact cleaning
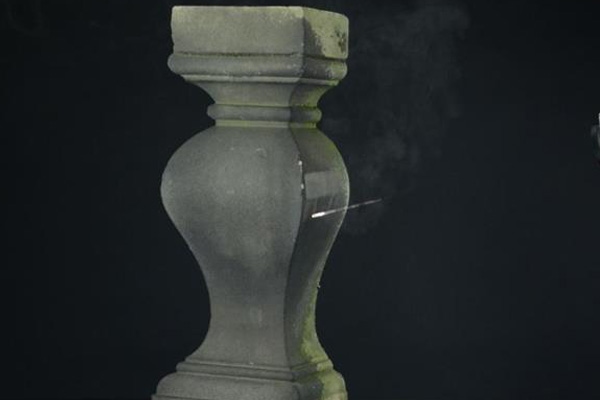

These applications typically use lower-power, carefully controlled laser systems and require expert oversight. While niche, they demonstrate the versatility of laser cleaning when precision is paramount.
10. Application Summary Table
| Application Area | Typical Contaminants | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Rust removal | Iron oxides | Minimal metal loss |
| Paint stripping | Industrial coatings | Layer selectivity |
| Welding prep | Oxides, oils | Improved weld quality |
| Mold cleaning | Carbon, polymers | Reduced downtime |
| Degreasing | Oils, fluids | Solvent-free cleaning |
| Surface prep | Mixed residues | Better adhesion |
| Maintenance | Corrosion, scale | On-site flexibility |
| Precision parts | Light contamination | Surface preservation |
Final Perspective: Understanding Laser Cleaning Applications Holistically
Laser cleaning machines are not defined by a single application. Their real strength lies in adaptability—serving as a controlled surface treatment across manufacturing, maintenance, and repair. The most successful users do not ask, “What can laser cleaning do?” They ask, “Where does surface control create the most value in our process?”
When that question is answered clearly, laser cleaning becomes more than a cleaning method—it becomes a strategic capability.
Identify the Right Laser Cleaning Application for Your Operation
Choosing the right laser cleaning application matters more than choosing the most powerful machine. BOGONG Machinery works with manufacturers and service providers to evaluate real materials, contaminants, and workflows, helping match laser cleaning systems to applications that deliver measurable results. If you want to understand where laser cleaning fits best in your operation—and where it does not—contact BOGONG Machinery for an application-driven discussion grounded in real industrial practice.
Talk to Bogong Laser Cleaning Machines ExpertsGet a Quote or Customized Solution for Your Application

-
Whatsapp: +86-15665870861
-
Email: info@bogongcnc.com